Self-Balancing Robot
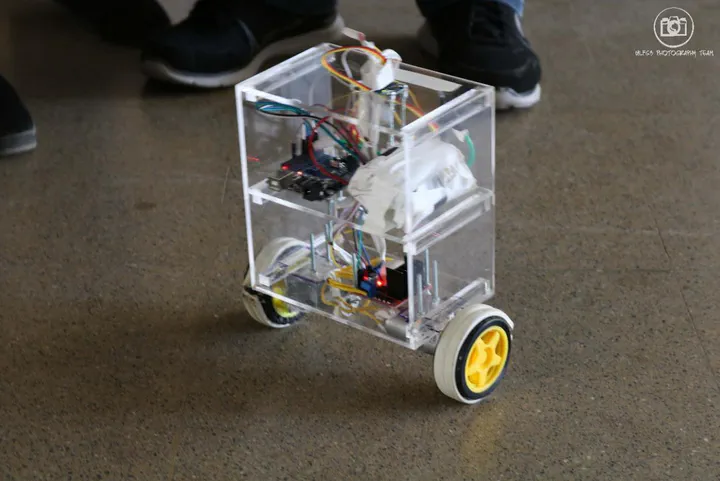
We developed a self-balancing two-wheeled robot using an Arduino and a MATLAB-based control design. The robot’s hardware consists of two wheels driven by DC motors, an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), and an Arduino microcontroller for real-time control. The primary objective of the project was to keep the robot balanced in an upright position while compensating for disturbances.
To design the control system, we built a dynamic model of the robot in MATLAB/Simulink, incorporating its physical parameters such as mass, wheel radius, and moment of inertia. Using this model, we applied state-space control techniques and designed a Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) for optimal stabilization. The control laws were tested in simulation before being implemented in the Arduino code.
The IMU measured the robot’s angle of inclination and angular velocity, and we used a complementary filter to combine these readings for accurate state estimation. The Arduino ran the control algorithm, calculating motor torque to keep the robot upright and correct any leaning. Fine-tuning the LQR gains was crucial for achieving smooth and stable balancing.
This project was completed as part of the “Automatic Control” course during my undergraduate studies. Teammates: Youssef Karout and Hassan Sleiman.